End-to-end MQ Lab
- Lab Overview
- Prerequisites
- Lab Environment
- 0 - Preparation
- 1 - Low Code / No Code Development with ACE Toolkit
- 2 - Generate the BAR file
- 3 - Deploy BAR file using ACE Dashboard
- 4 - Testing the API
- Summary
Lab Overview
IBM MQ can transport any type of data as messages, enabling businesses to build flexible and reusable architectures. It works with a broad range of computing platforms, applications, web services and communications protocols for security-rich message delivery. IBM MQ provides a communications layer for visibility and control of the flow of messages and data inside and outside your organization.
This session explains the steps need to create an Integration Flow developed with ACE Toolkit that uses the REST API functionality as well as the MQ Nodes to interact with an MQ Queue Manager using the latest version of the ACE Integration Server Certified Container (ACEcc) as part of the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I).
Lab’s takeways:
- Creating an integration flow that connects to a message queue
- Deploying the integration flow as a container in Kubernetes
- Checking the message using MQ Web Console
Prerequisites
- You need to have an OpenShift environment with CP4I. For this session, your proctor will provide you a pre-installed environment, with admin access (more details below). If you want to create your personal environment, you can request an environment on IBM TechZone.
- You should have an MQ Queue Manager runtime pre-created in your CP4I on ROKS environment.
- You need to have the IBM App Connect Enterprise Toolkit installed in your desktop. Follow the sections Download IBM App Connect Enterprise for Developers and Install IBM App Connect Enterprise from this tutorial to install it.
- You need to download the OpenAPI spec. Open this page and save as swagger.json. You will use this spec later in the lab.
Lab Environment
For this session you will use a ROKS 4.10 environment with Cloud Pak for Integration 2022.2. For this section, your lab proctors pre-installed this cluster for you with a pre-configured IBM MQ instance.
0 - Preparation
In this section you will do some initial steps to prepare your environment for the lab.
Next steps, assume that you already accepted the Account invitation in IBM Cloud (account: 2543884 - itztsglenablement05). This is the same account of GitOps lab. If you didn’t accept, please check the GitOps lab preparation section to complete it.
Log in IBM Cloud.
In IBM Cloud dashboard, change your IBM Cloud account to 2543884 - itztsglenablement05.
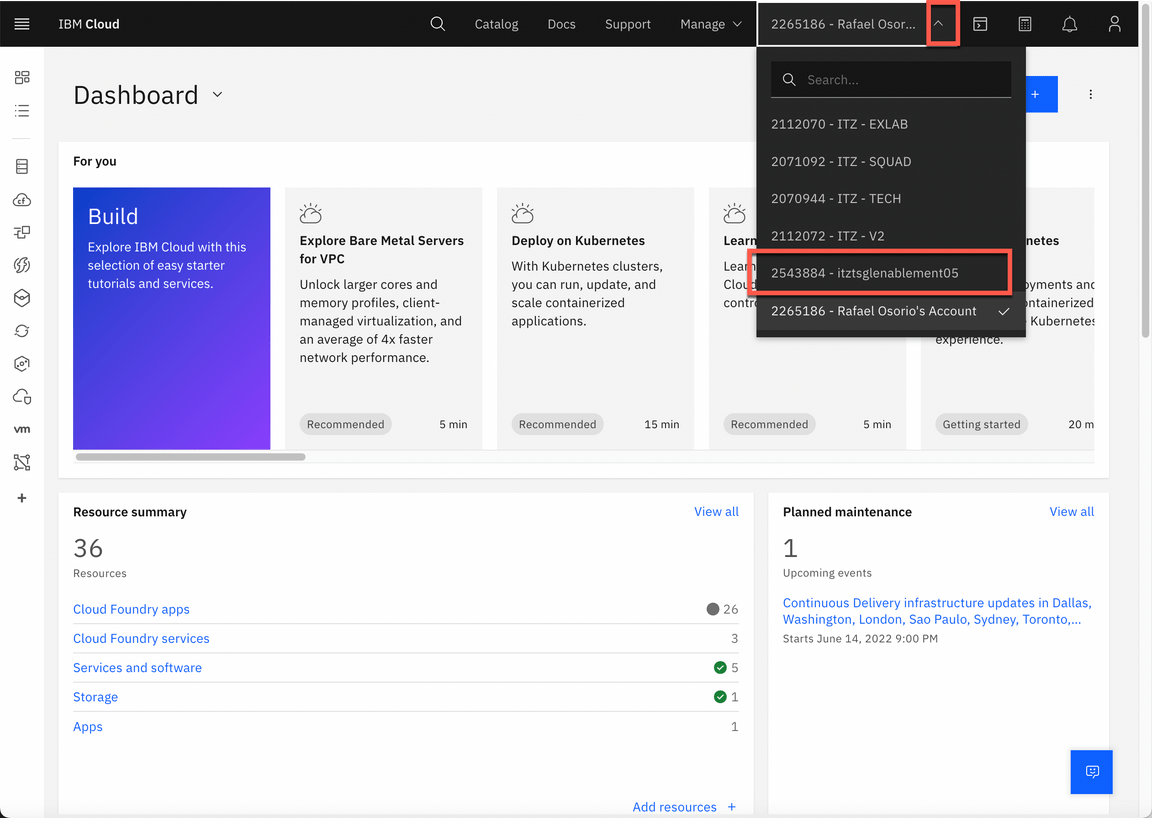
Now, click here to open the Team Environments page.
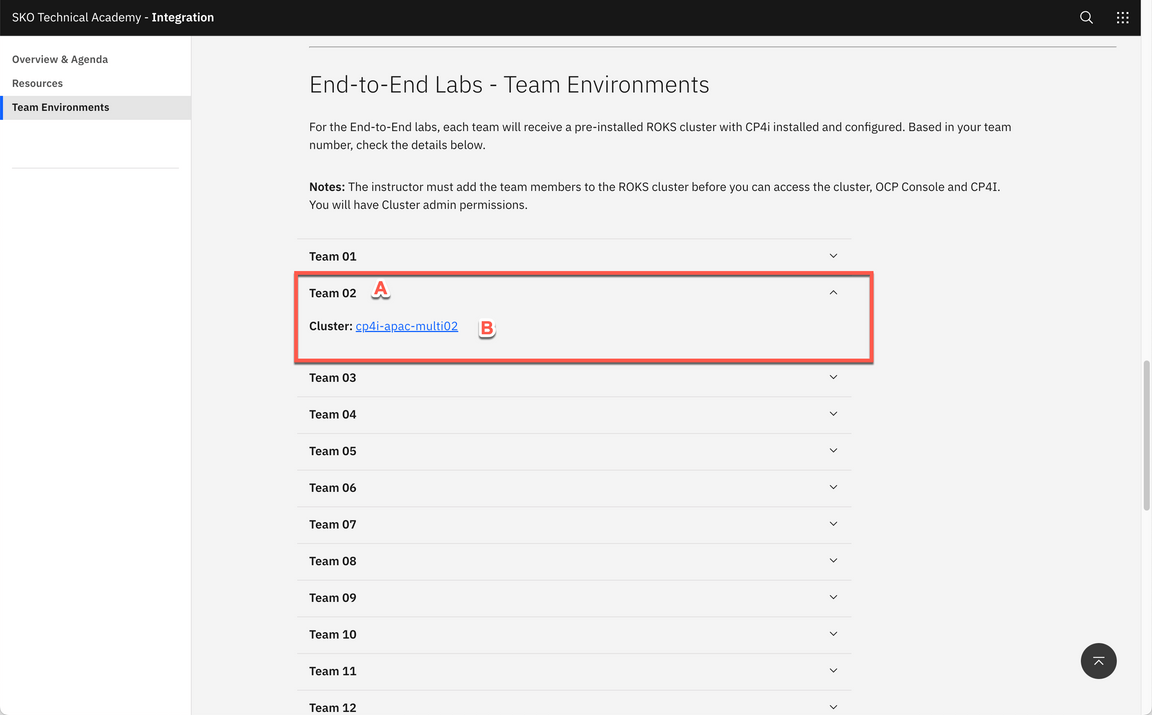
Click to go to the End-to-End Labs - Team Environments.

- Open your Team’s section (A) (check the number of your team with the Lab’s proctors). Then, open your team’s Cluster page (B).
- On your cluster’s page, click OpenShift web console.
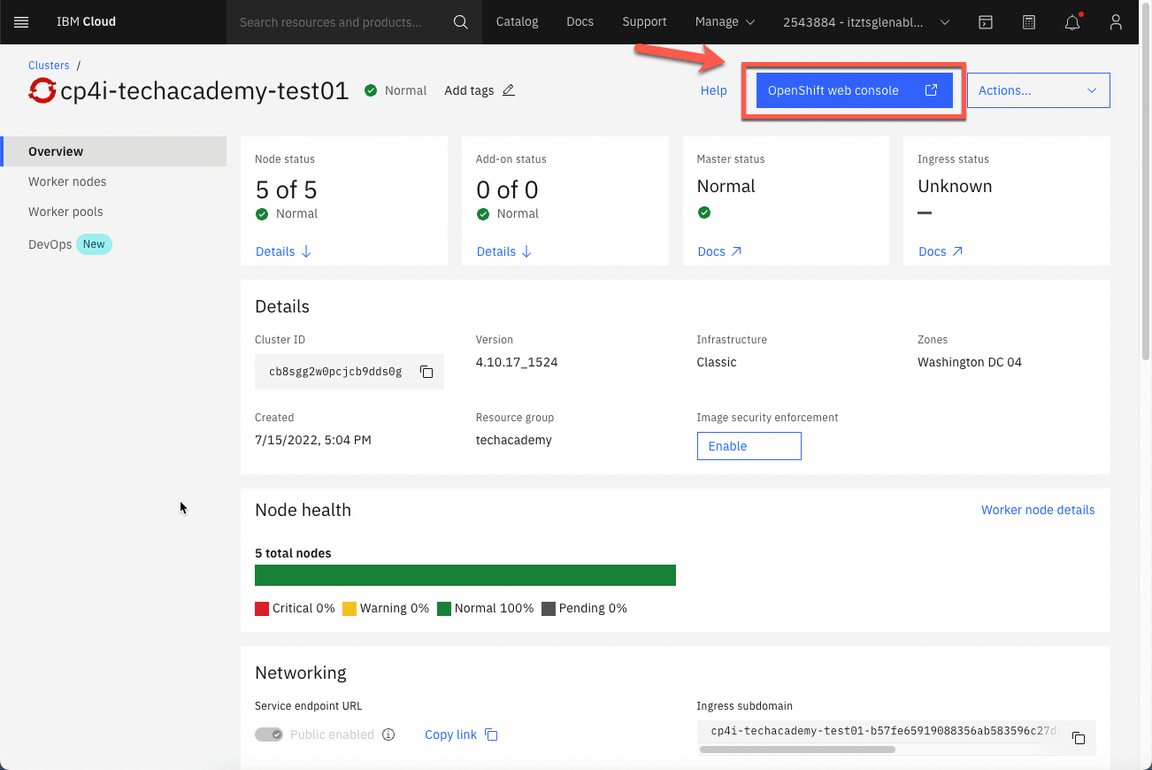
- Great, now let’s check your Cloud Pak for Integration environment. First we need to get the Platform Navigator URL and password. Let’s do it! Back to the OpenShift Web Console, open Workloads (A) and Secrets (B) again.
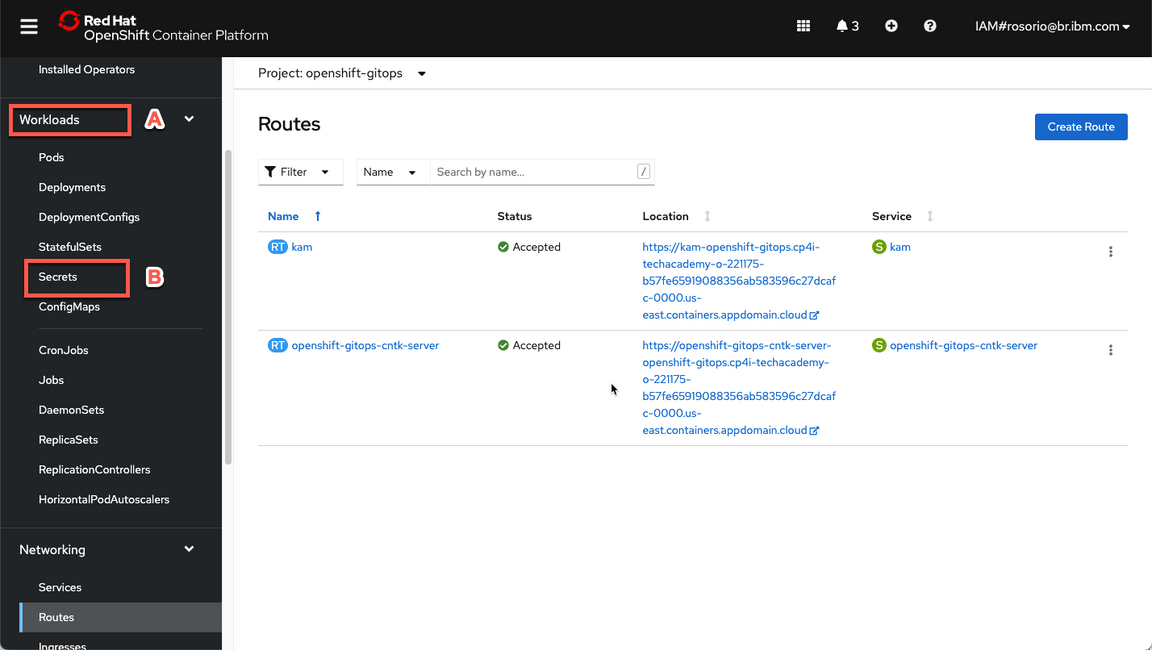
- Now filter by cp4i project (A) and open the ibm-iam-bindinfo-platform-auth-idp-credentials secret (B).
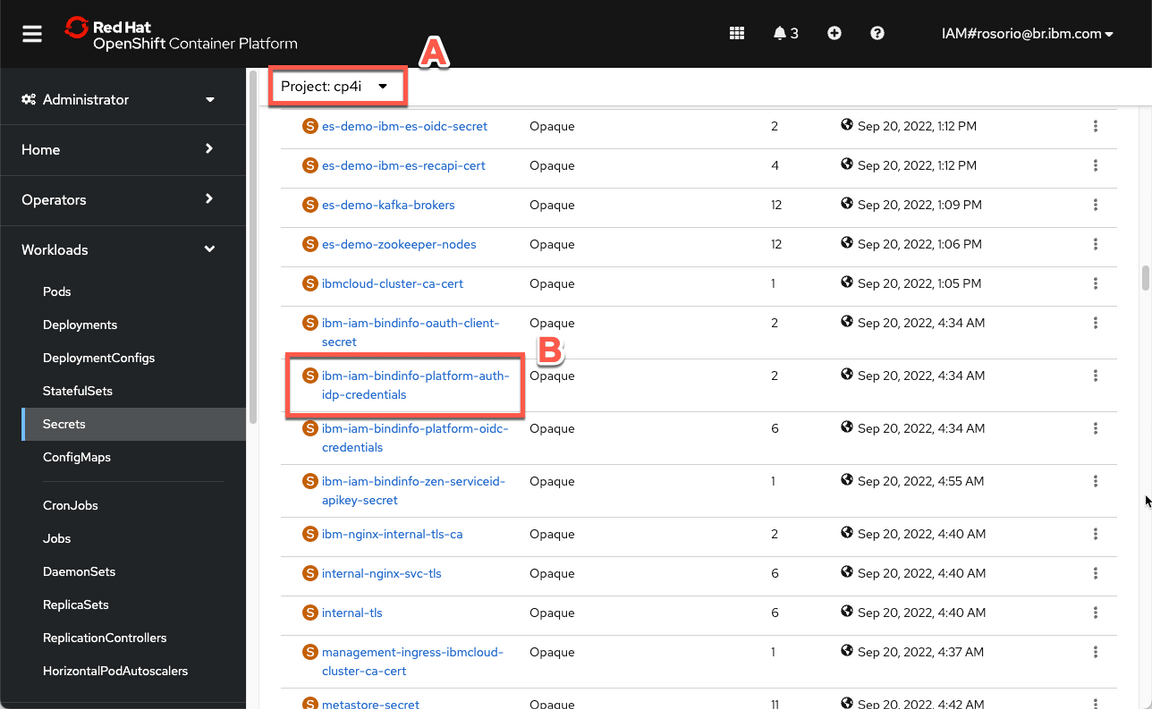
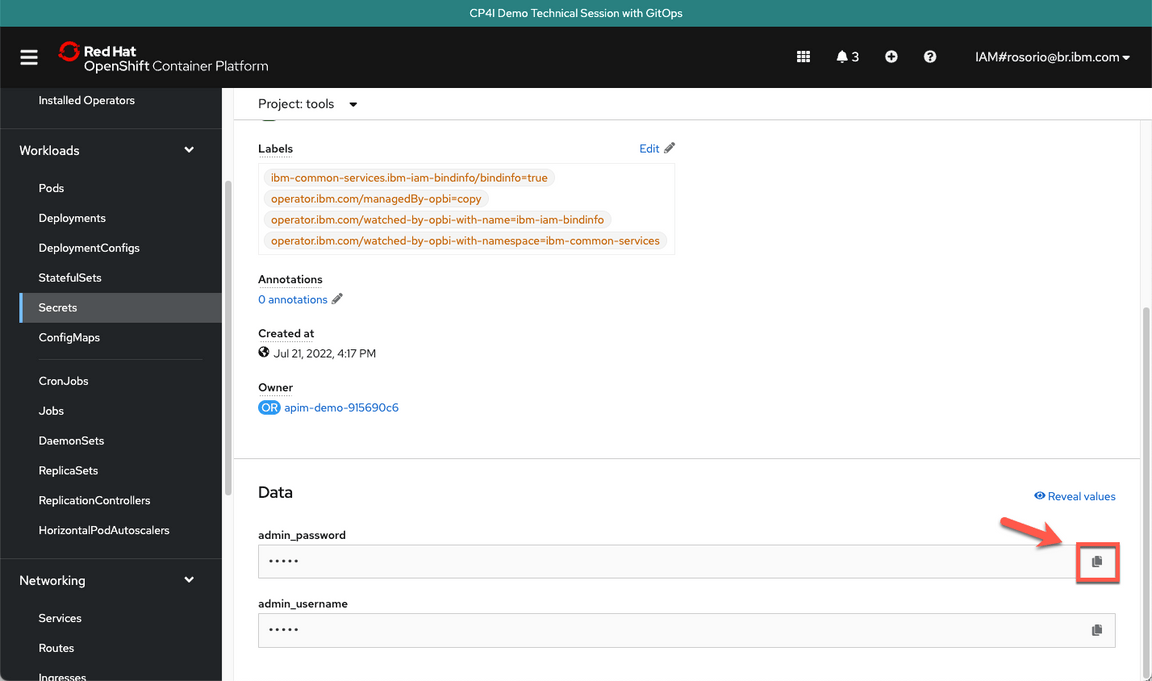
- Scroll down and click to copy the admin_password. You are welcome to take note of this password.
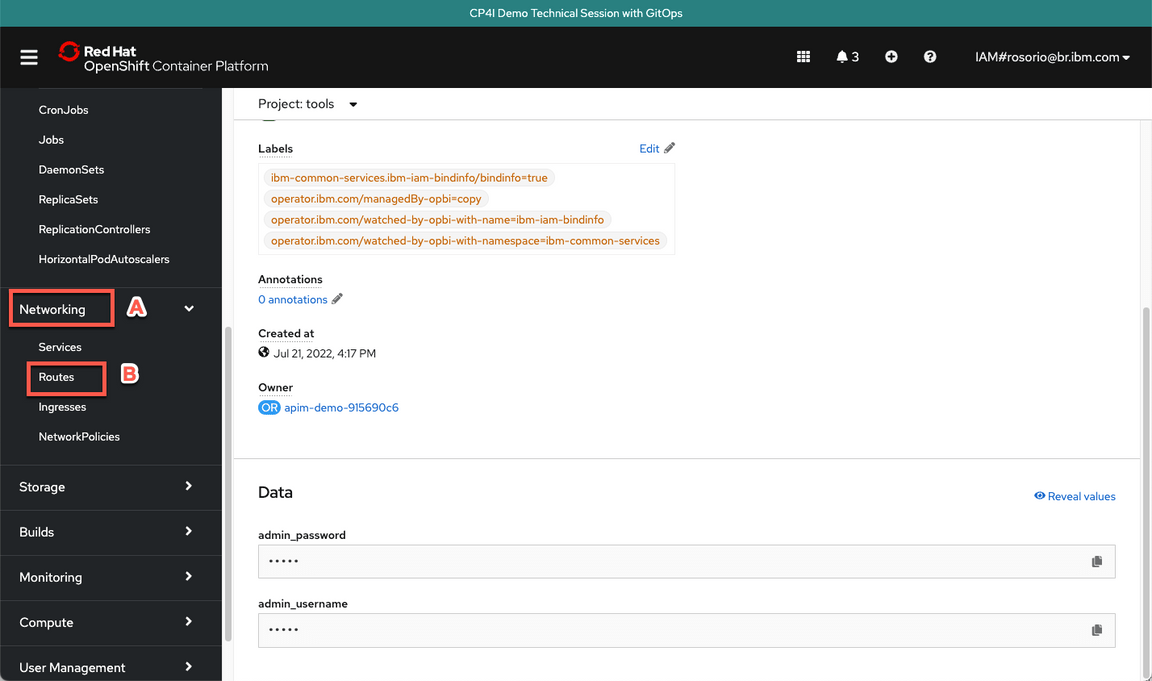
- Now, let’s get the Platform Navigator URL. Open Networking (A) and Routes (B).
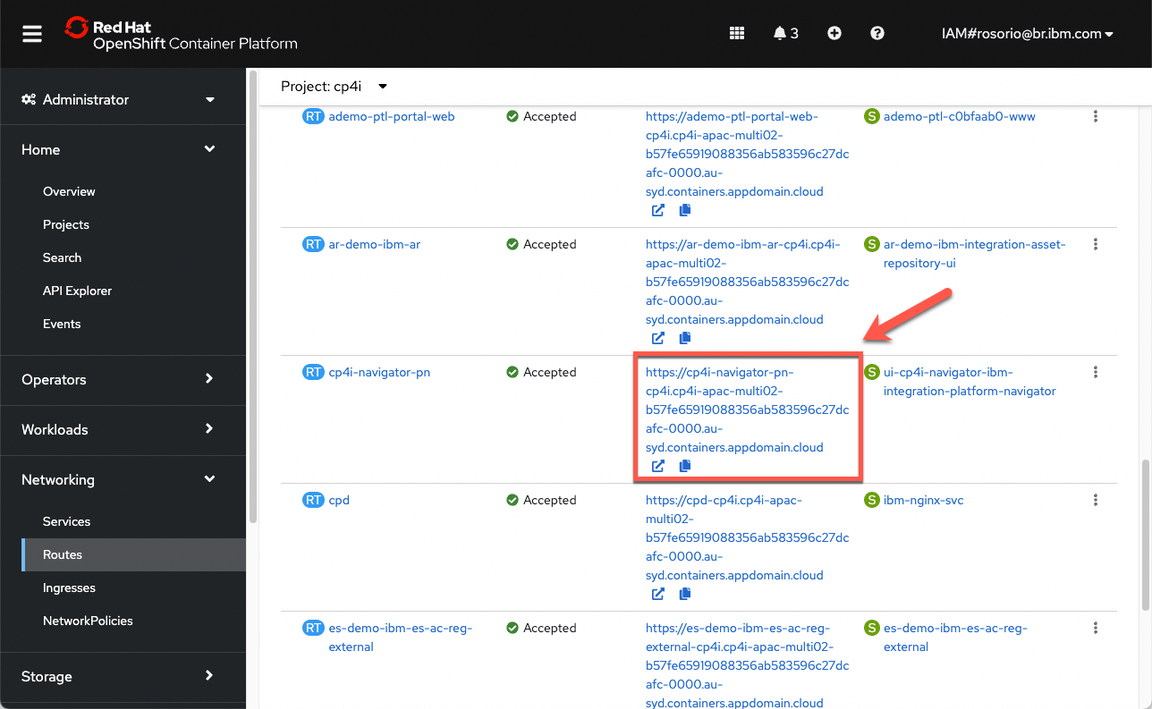
- Scroll down and click on the cp4i-navigator-pn location to open the Platform Navigator.
- If necessary, accept all the risks, and click IBM provided credentials (admin only) link.
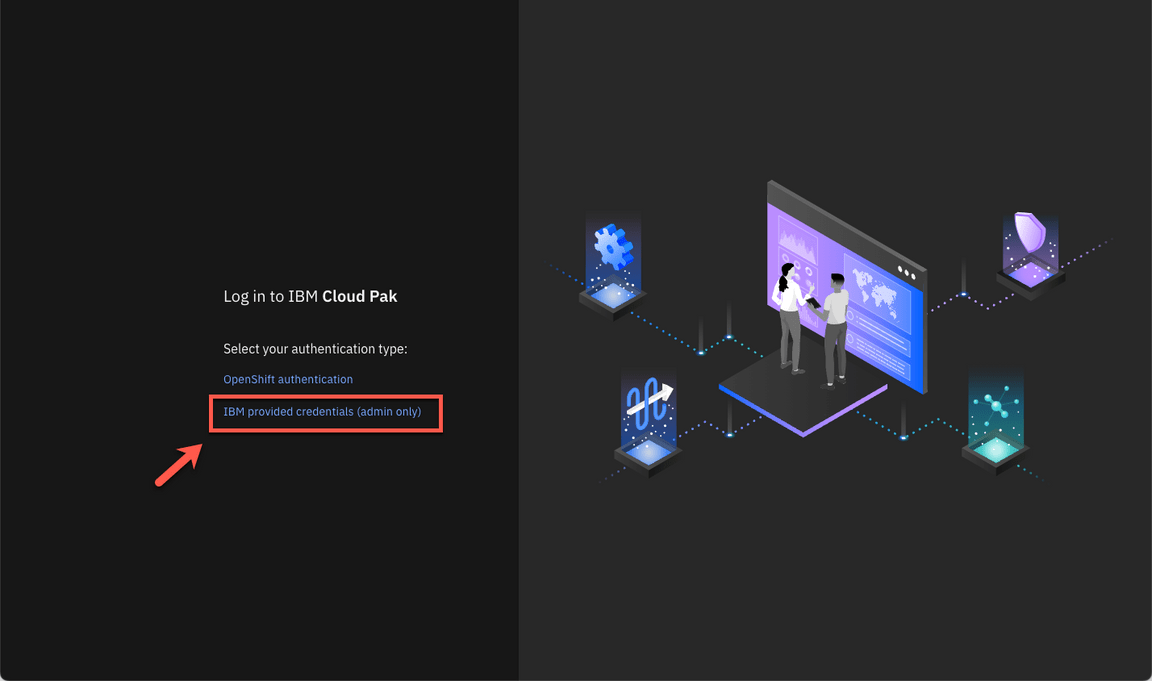
- Log in with admin user and the password that you copied in the previous step.
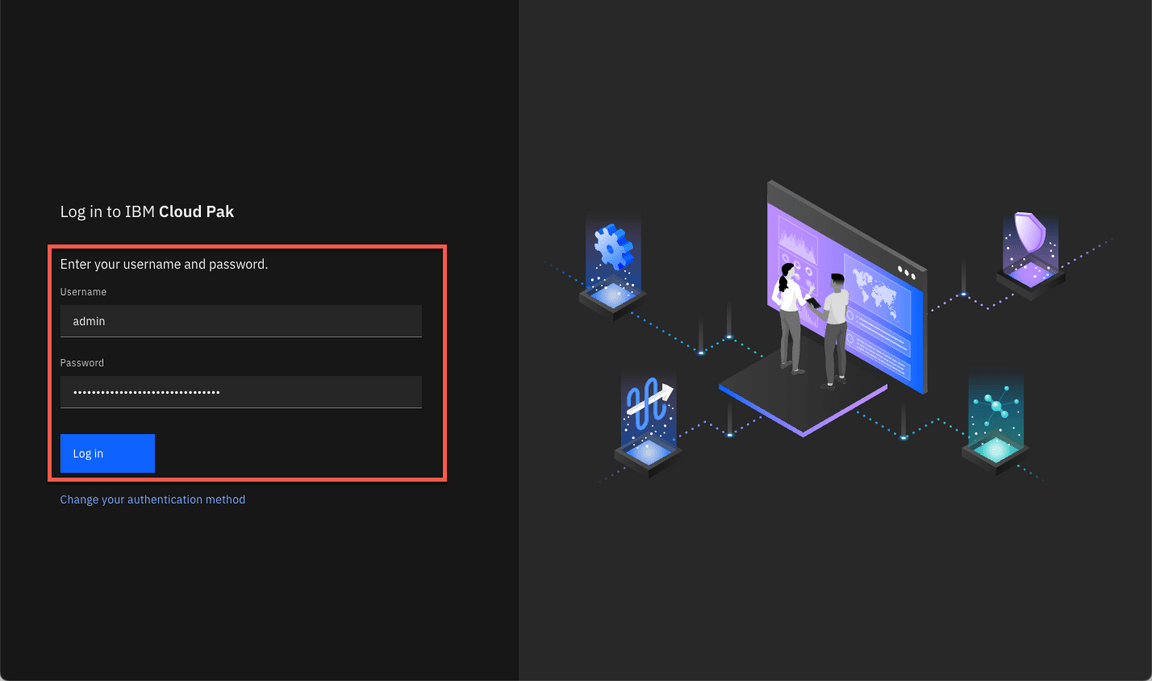
- Close the Welcome dialog. Great, now you are ready for the lab. Enjoy it!
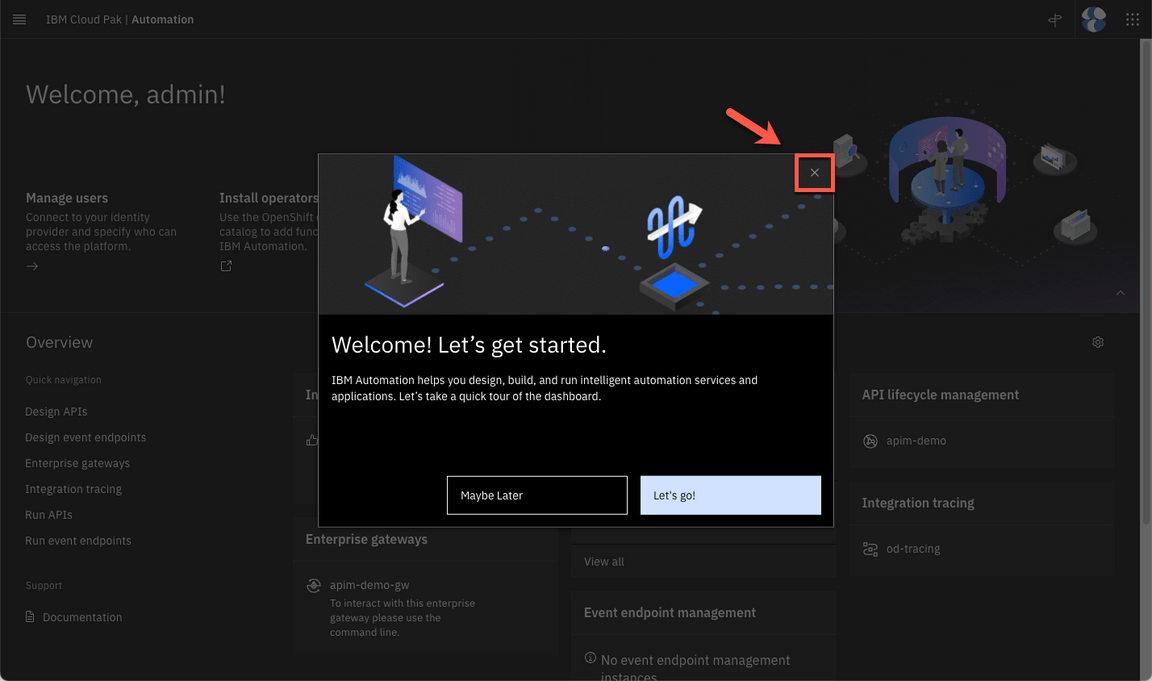
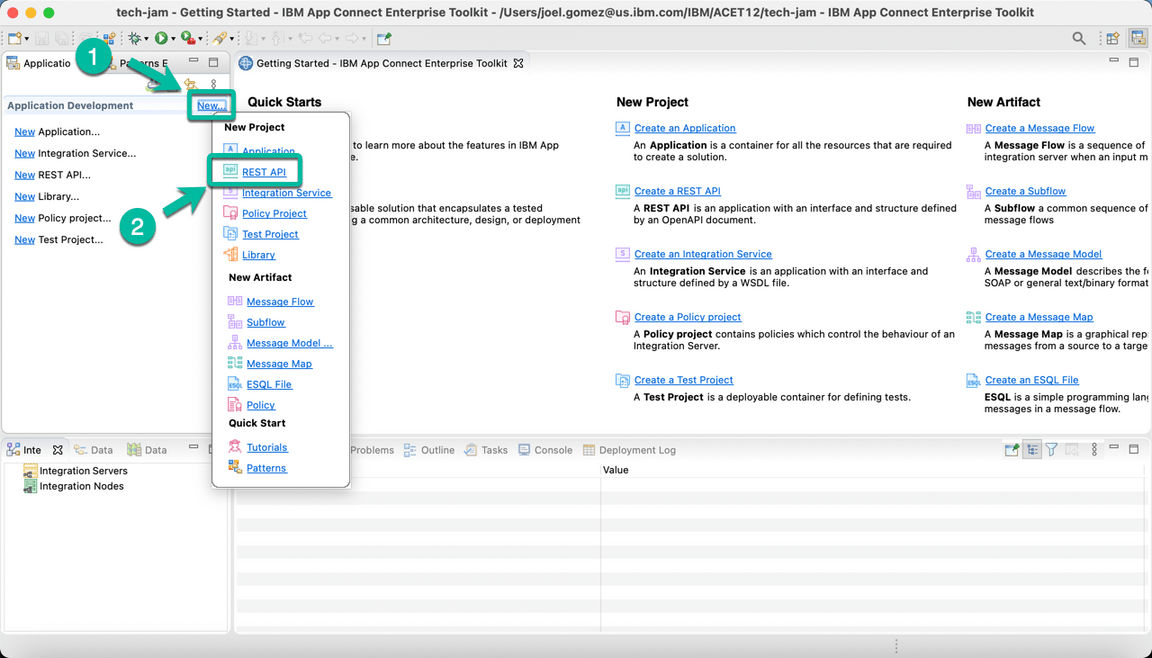
1 - Low Code / No Code Development with ACE Toolkit
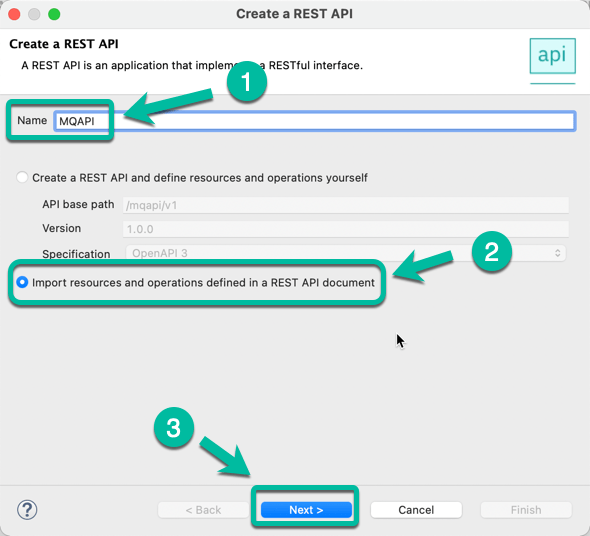
- Open the Toolkit in your workstation and create a new REST API project as shown below.
- Give a name to your project, i.e. MQAPI and then select the option to Import resources since we will leverage a definition already created.
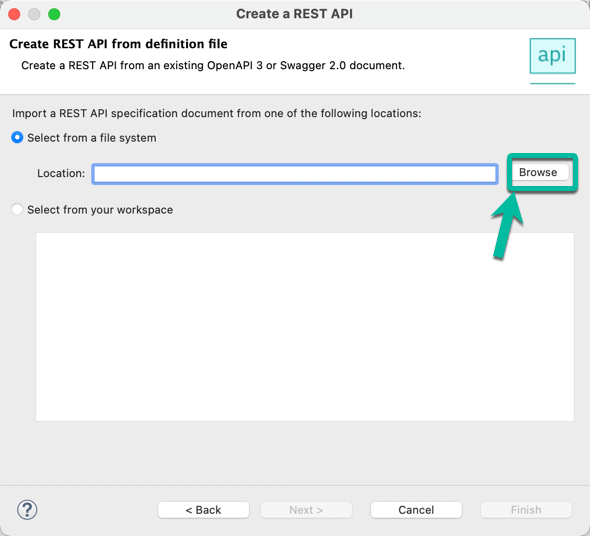
- In the wizard click Browse and navigate to the location where the OpenAPI file definition is located.
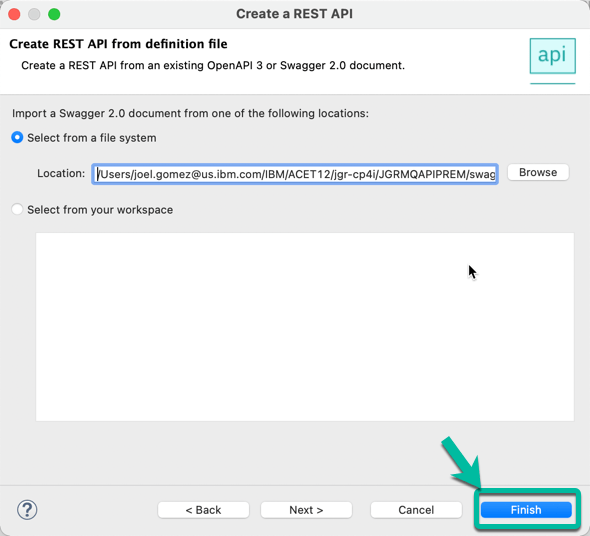
- Once the path is displayed in the Location field click Finish.
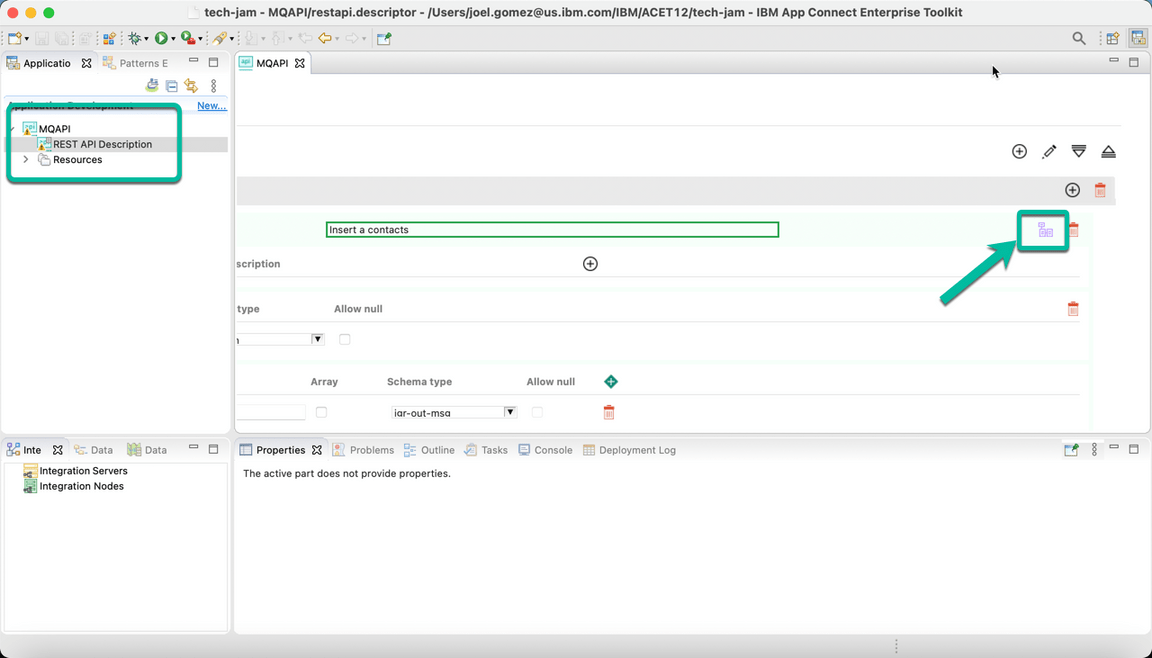
- The REST API will be displayed, scroll to the right if needed to open the sunflow operation as shown in the image to proceed to implement the API logic.
- The Message Flow Editor will be open with only the Input and Output terminals. Double click the tab to maximize the editor and work with the flow.
- Drag and drop the Nodes from the palette to implemeng the “logic”. In this case we will use the following nodes:
Flow Order Node,
HTTP Header Node,
MQ Header Node,
MQ Output Node, and
Mapping Node.
And you will proceed to wire them. The flow should look like the one below. Once you are done double click the tab again in order to access the properties for each node.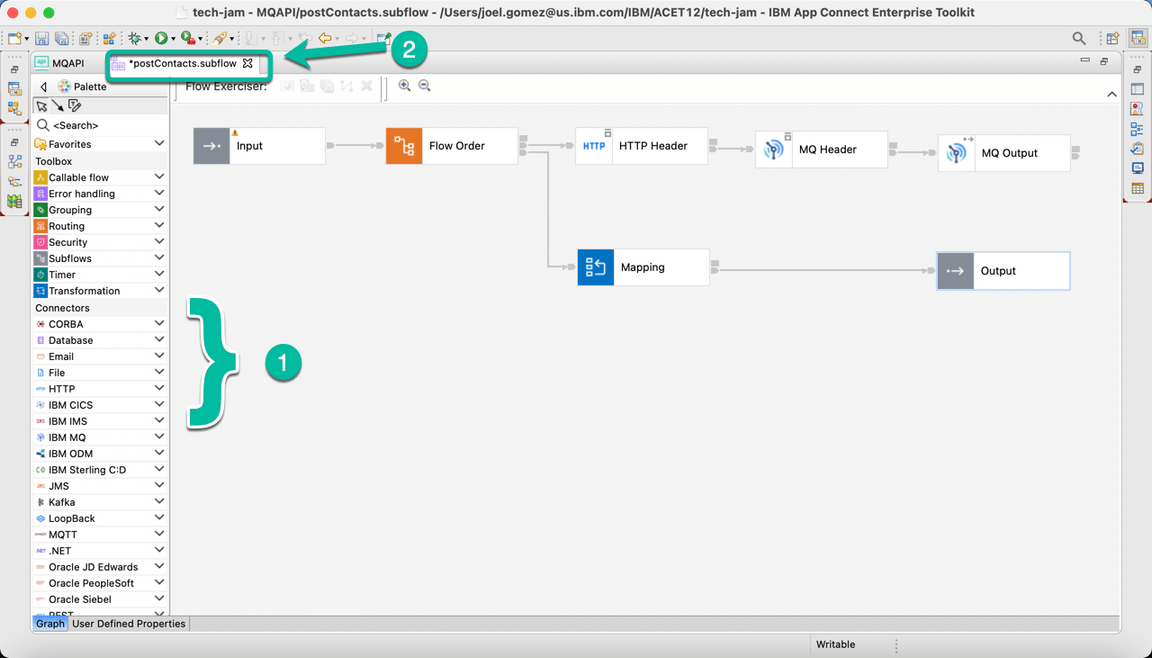
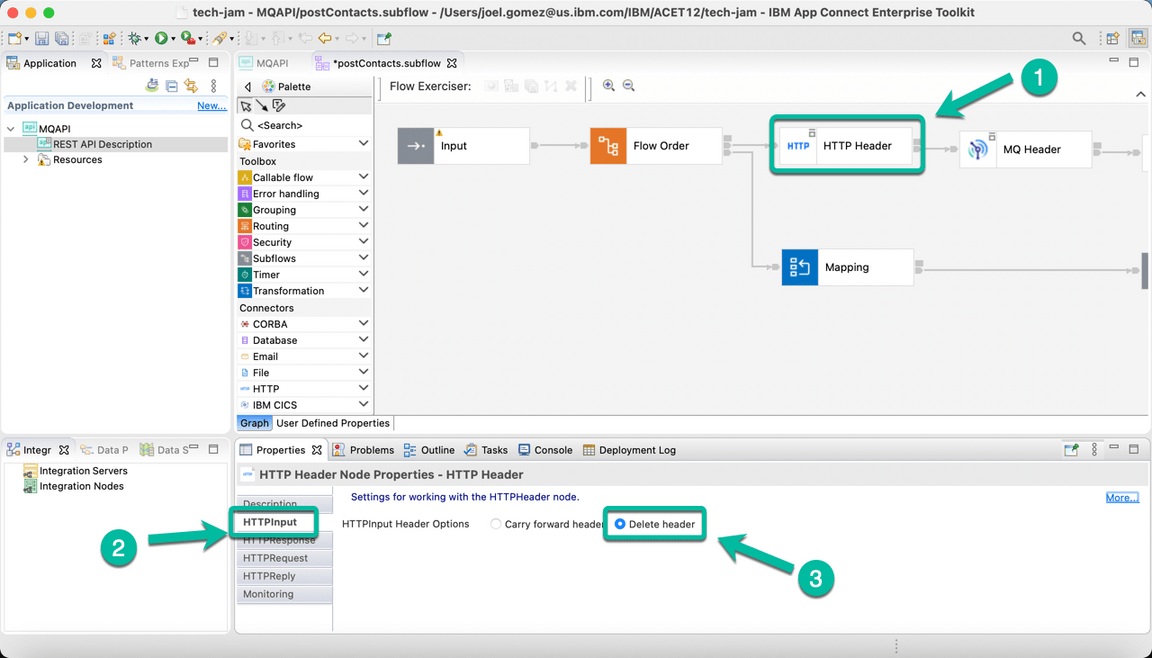
- Now we will configure each node, starting with the HTTP Header Node. Click on it to bring it to focus and then select the HTTP Input tab followed by the Delete header option as shown below.
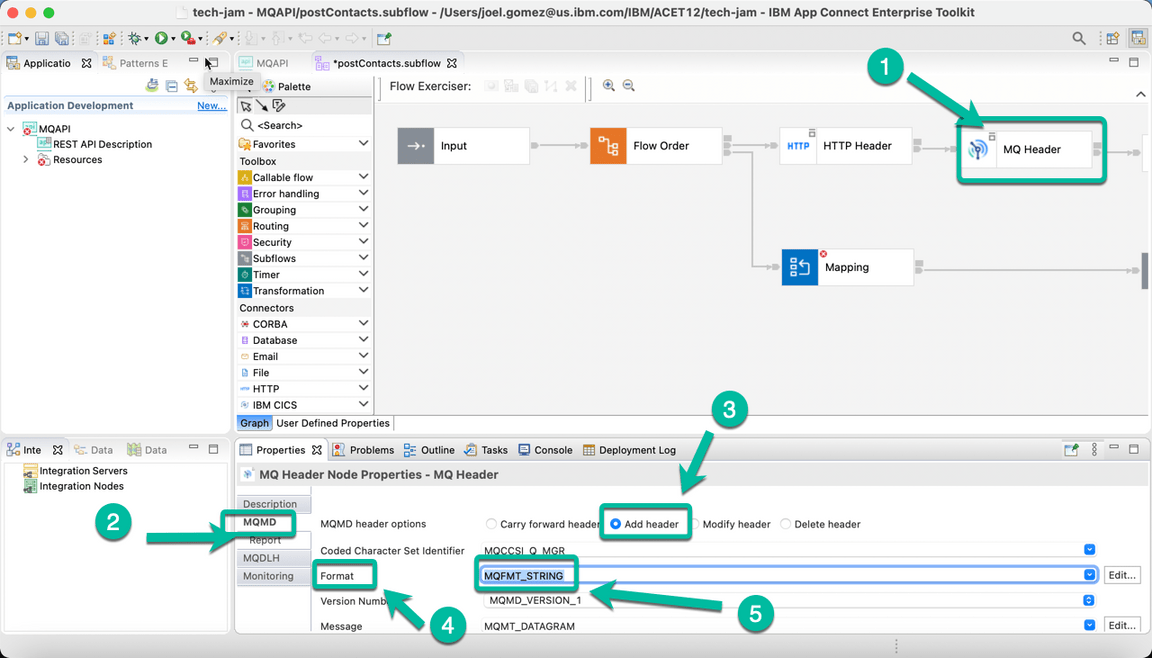
- Now select the MQ Header Node and navigate to the MQMD tab enabling the Add header option. And selecting MQMFT_STRING for the Format field as shown below.
- Then select the MQ Output Node and in the Basic tab enter the name of the queue we will use to put the messages, in this case CP4I.DEMO.API.Q
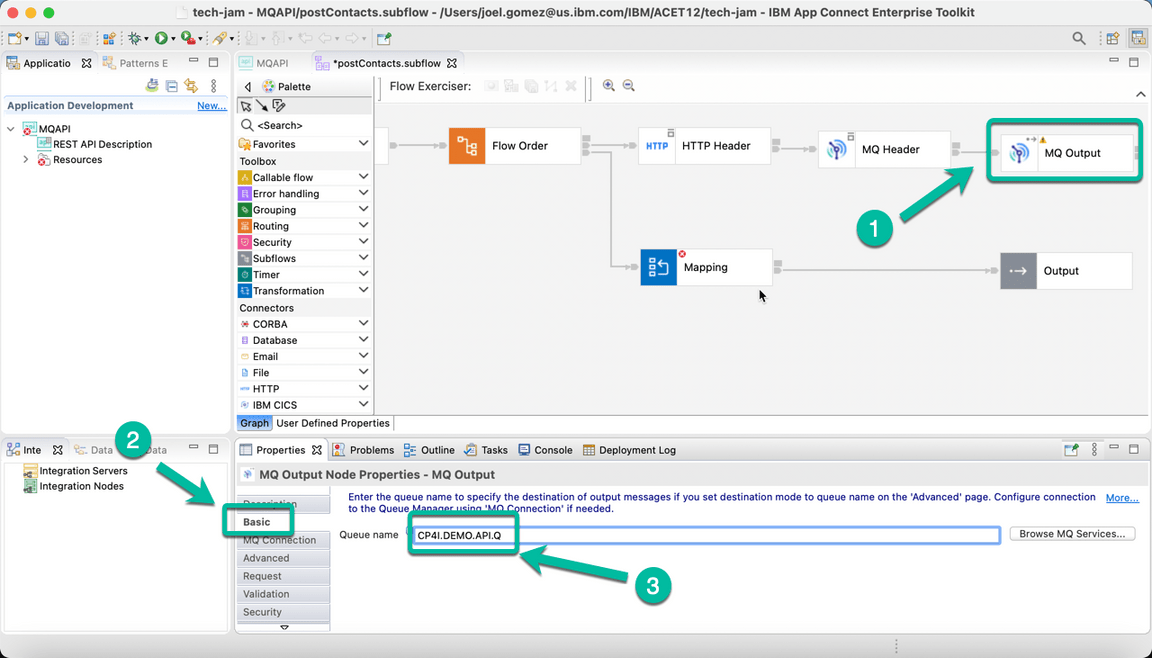
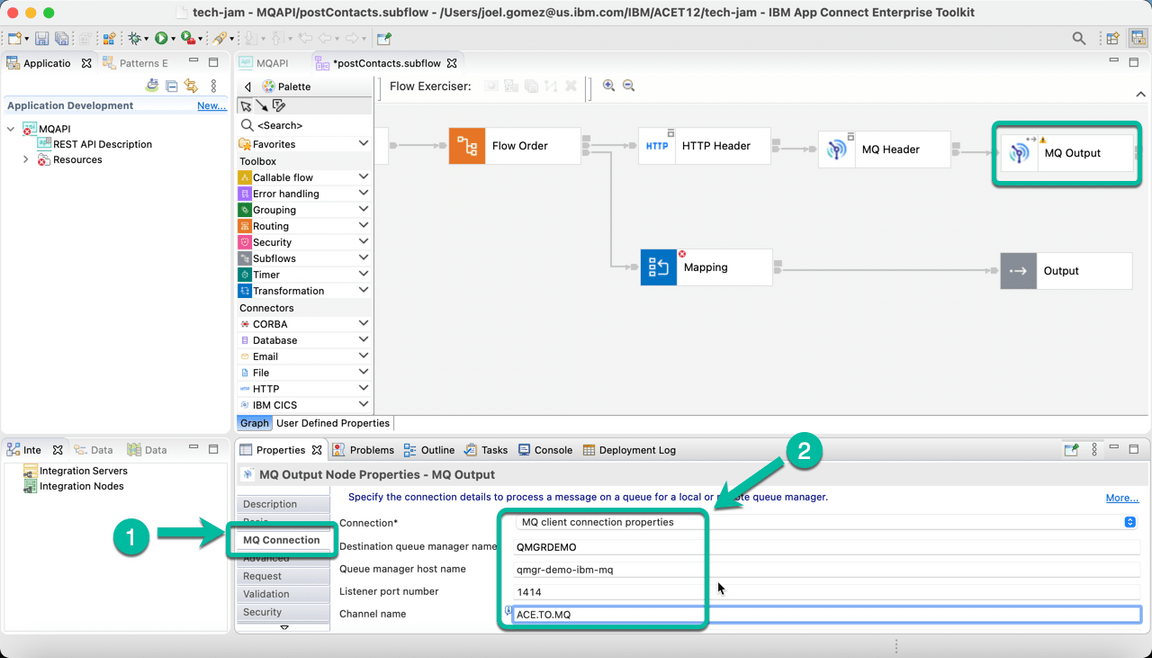
- In the same MQ Output Node navigate to the MQ Connection tab enter the information to connect to the Queue Manager. The information is based on the configuration we used for MQ, and for simplicity is included below.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Connection | MQ client connection properties |
| Destination queue manager name | QMGRDEMO |
| Queue manager host name | qmgr-demo-ibm-mq |
| Listener port number | 1414 |
| Channel name | ACE.TO.MQ |
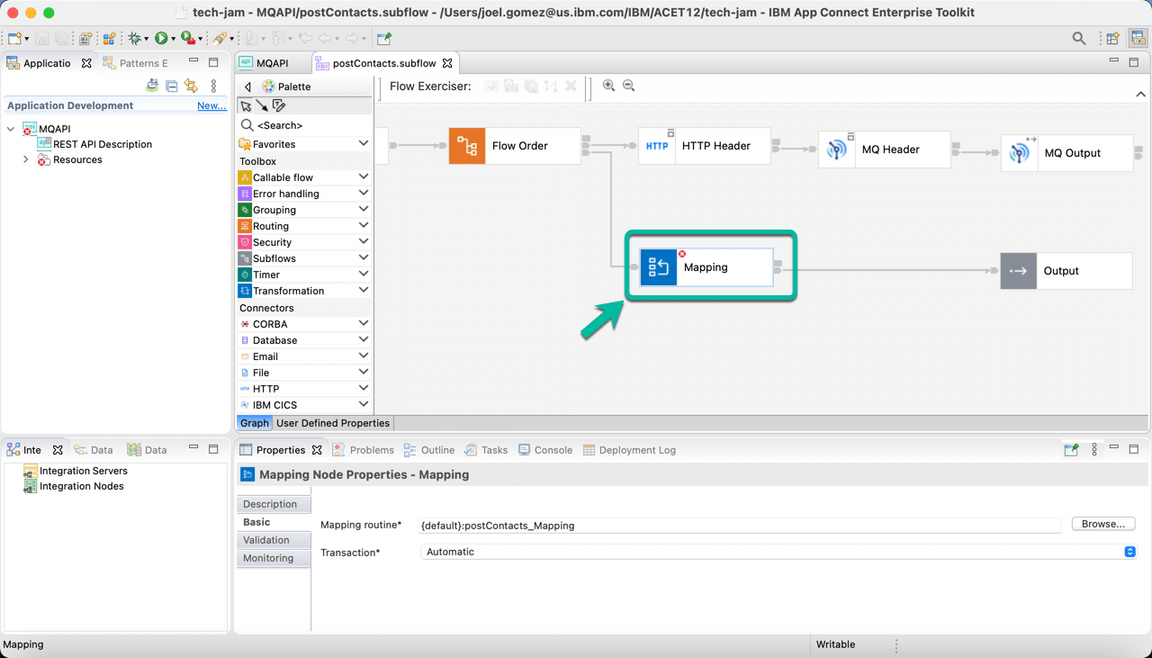
- Now double click the Mapping Node,
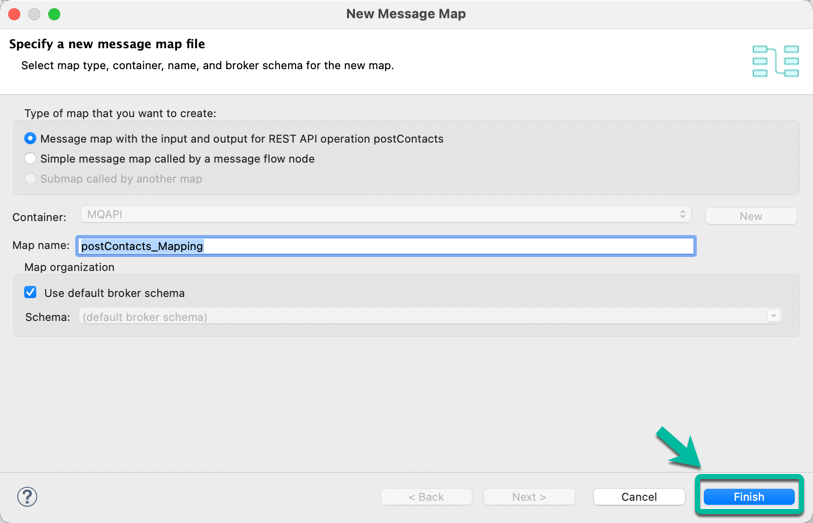
- In the wizard window simply click Finish.
- Expand the JSON section in both the input and output message assemblies and connect the payload as shown below.
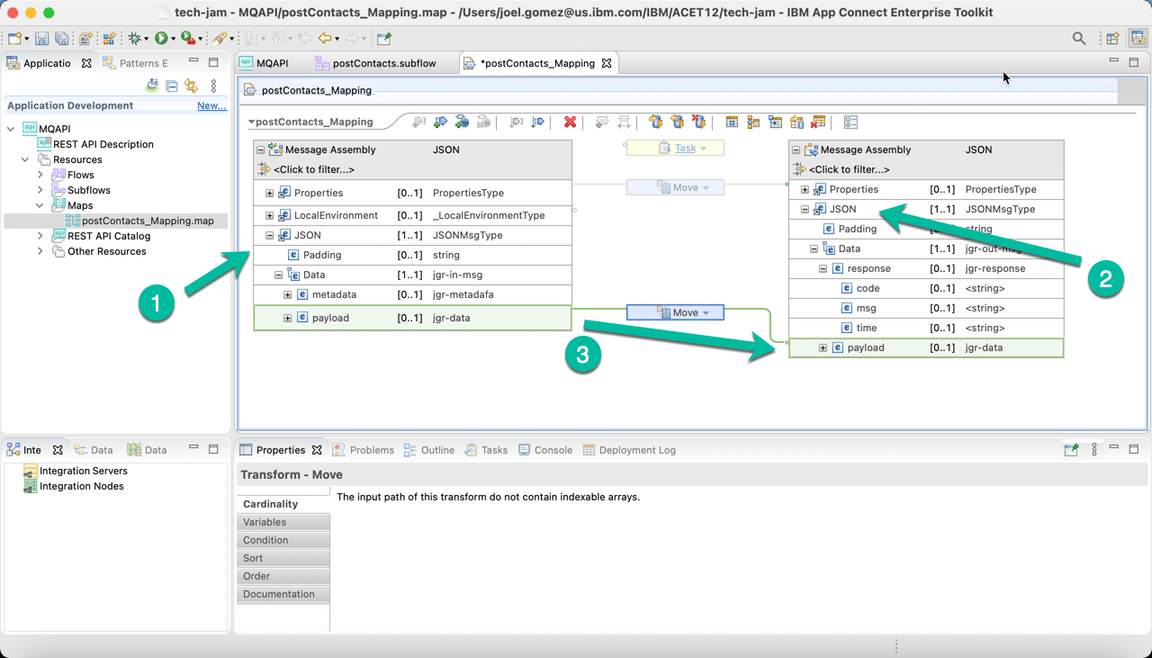
- Then right click the code field and select Add Assign from the menu.
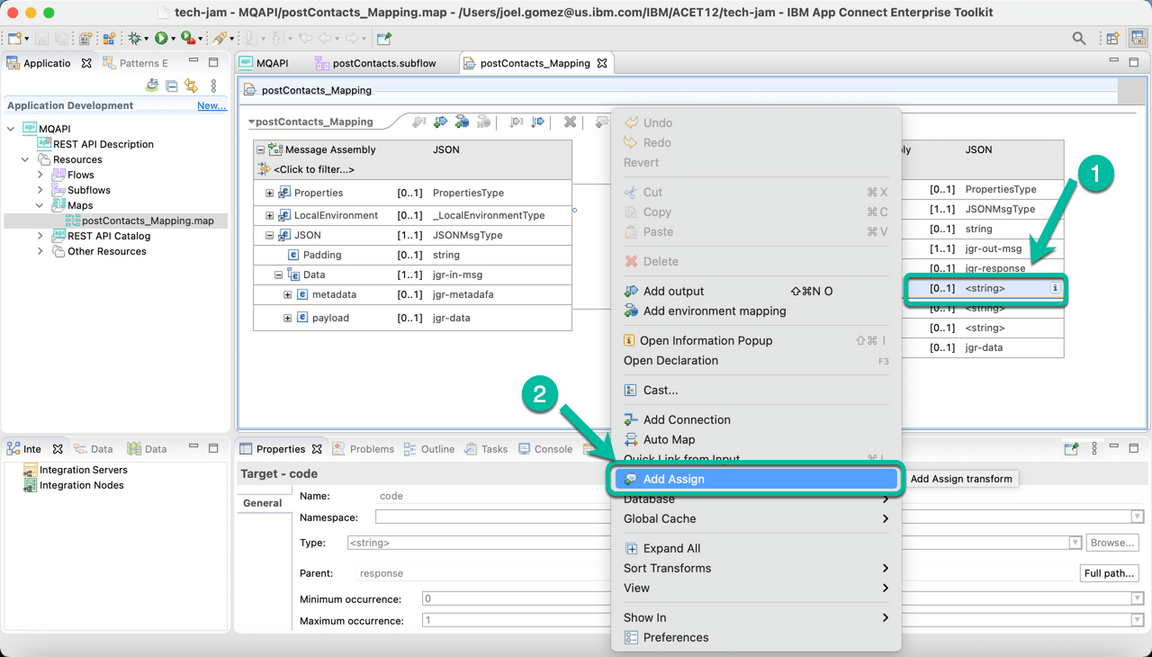
- In the properties section enter CP4I0000 in the value field.
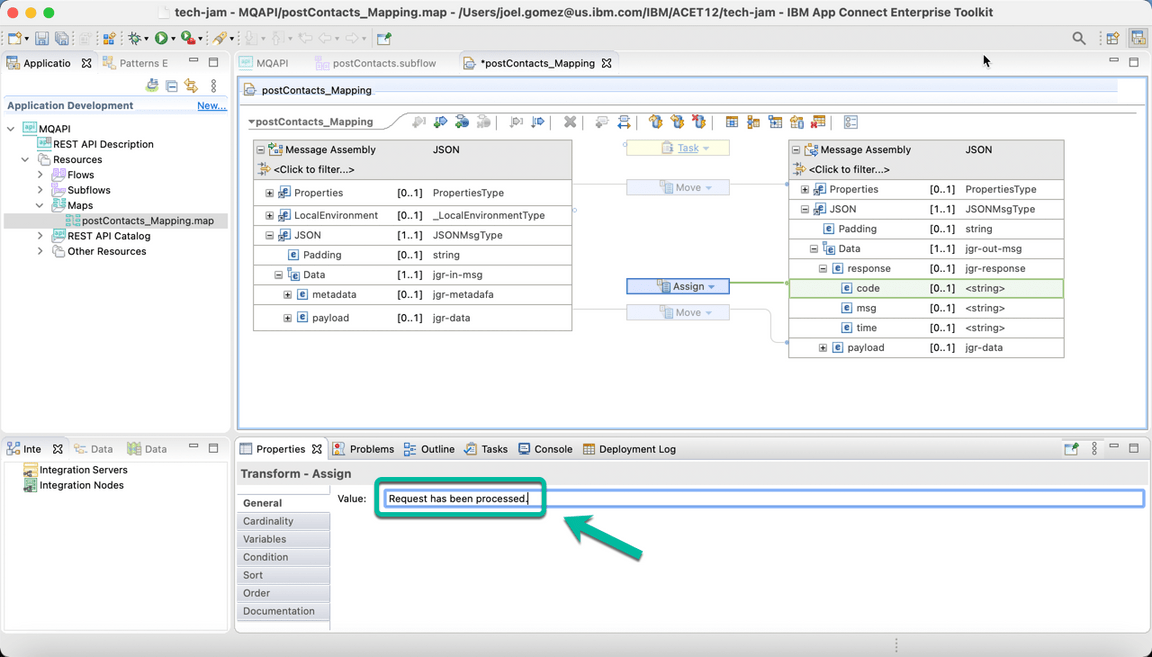
Repeat the same process for field msg and assign the value Request has been processed
Do the same for field time but this time we will replace the Assign option with the current-time function as shown below.
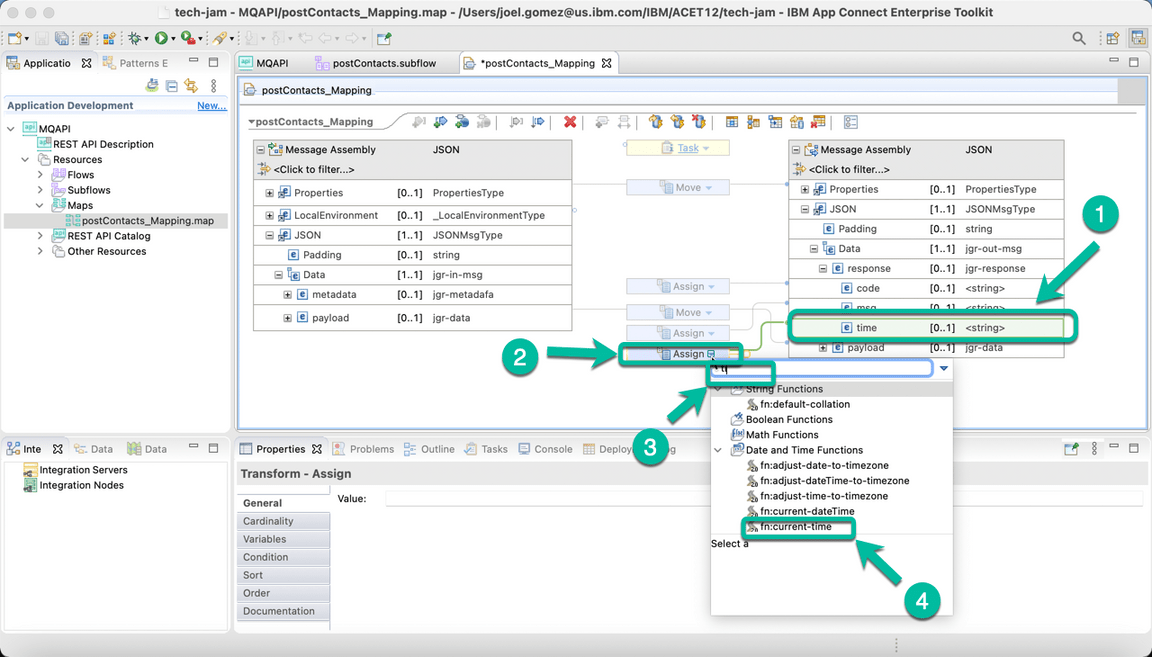
- The integration flow is completed. Save your progress and close the mapping tab.
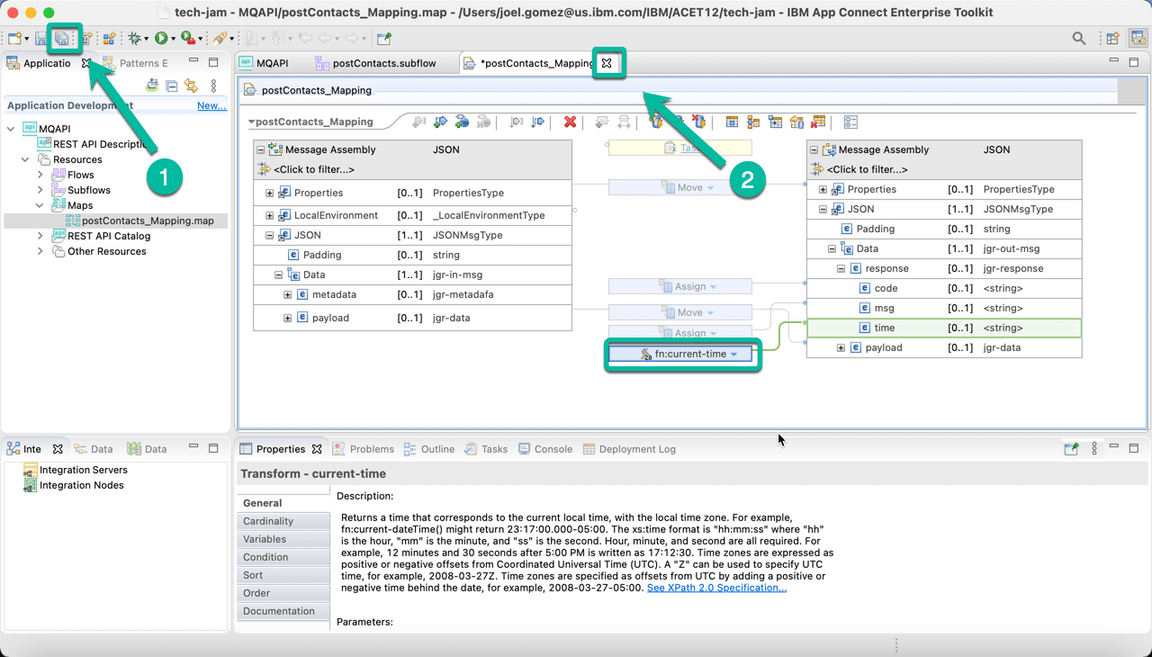
2 - Generate the BAR file
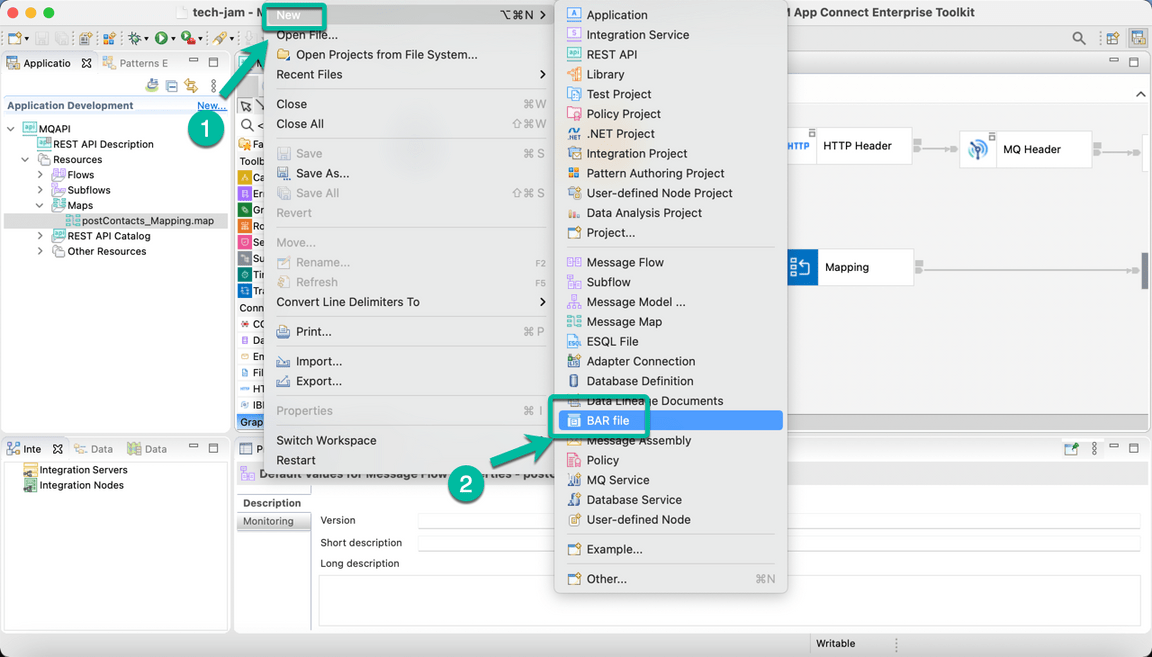
- Now we will generate the BAR file that we will use to deploy the Integration into CP4I. From the File menu select New and then BAR file as shown below.
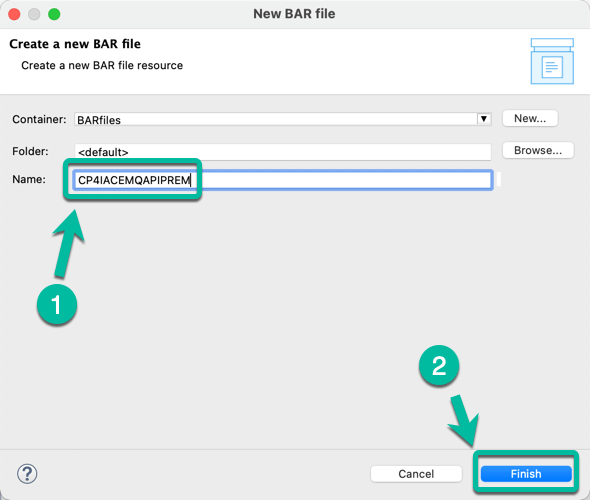
- In the pop up window enter the name of the BAR file, in this case CP4IACEMQAPIPREM. And then click Finish.
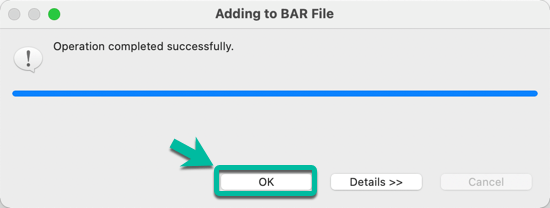
- Click OK in the confirmation window.
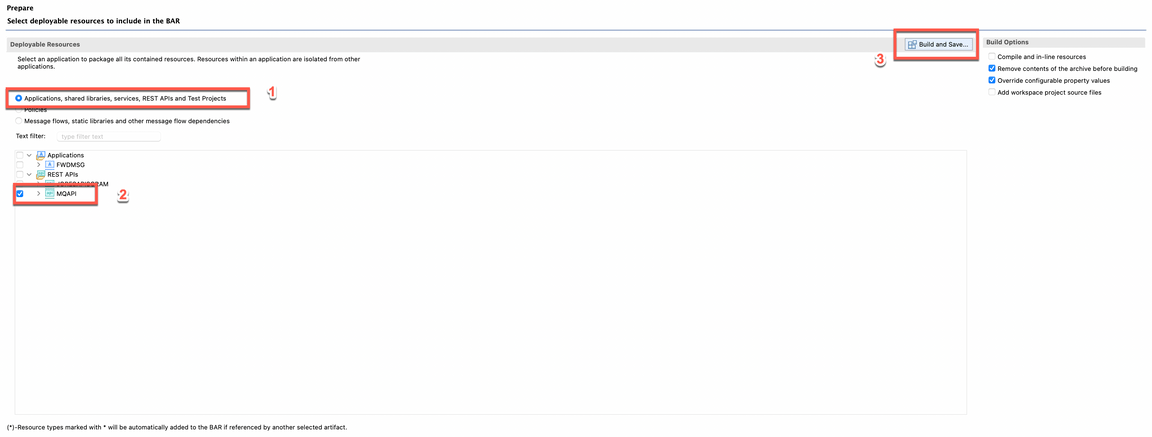
- The BAR Editor is open. Select Applications, shared libraries, services, REST APIs, and Test Projects to display the right type of resources and then select your application, in this case MQAPI. Finally click Build and Save… to create the BAR file.
- You can dismiss the notification window reporting the result clicking OK.
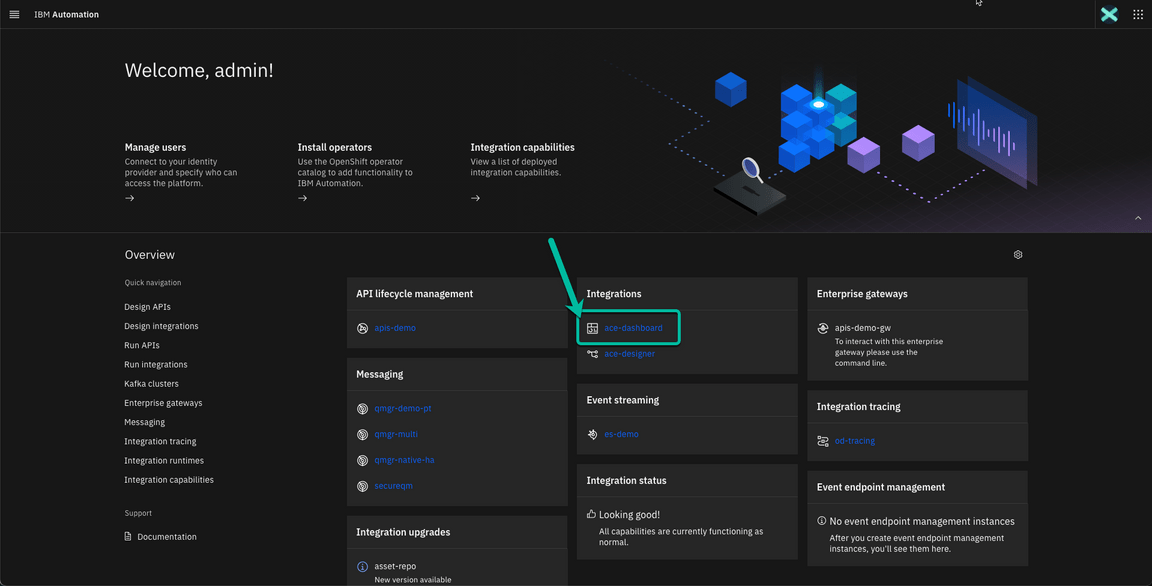
3 - Deploy BAR file using ACE Dashboard
- Back to Platform Navigator, open the ACE Dashboard.
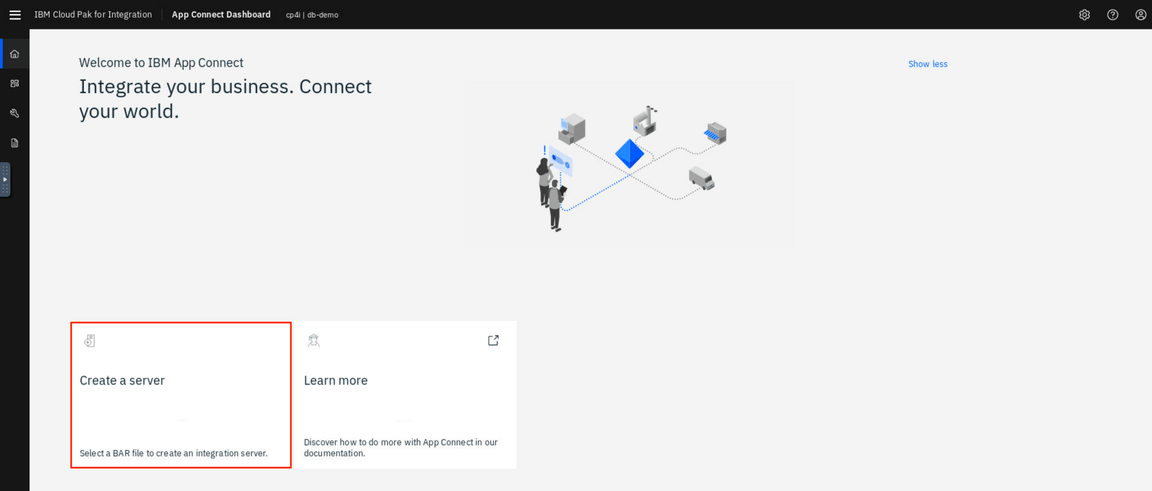
- To deploy a BAR file, you need to create an Integration server. Let’s do it! Click Create a server.
- This will start the deployment wizard. Select the Small Integration tile and then click the Next button.
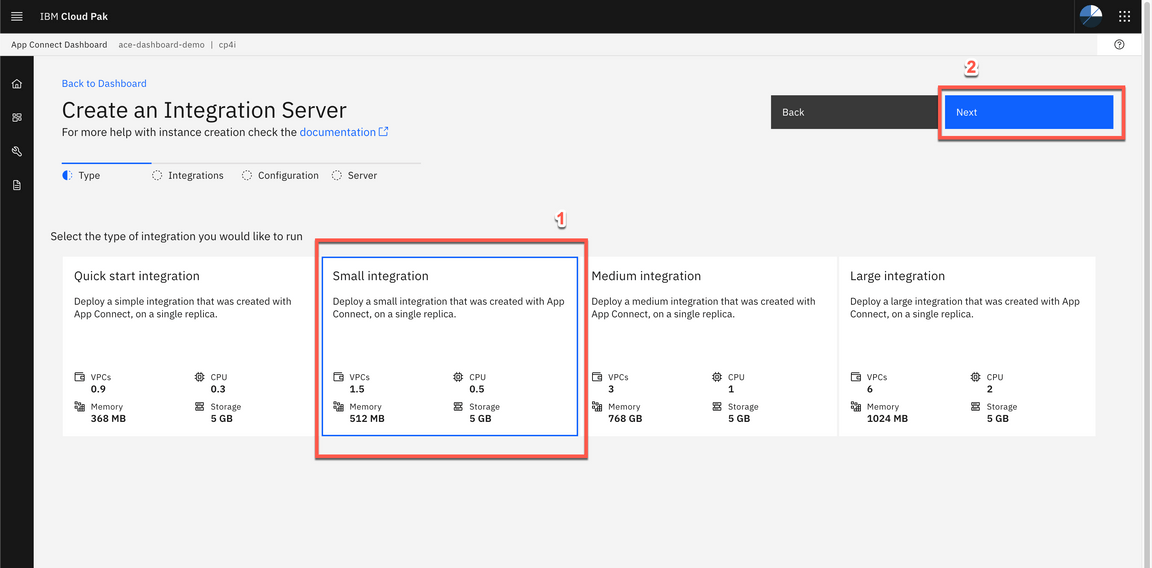
- Click to upload your BAR File. And select the MQAPI.bar. And click Next.
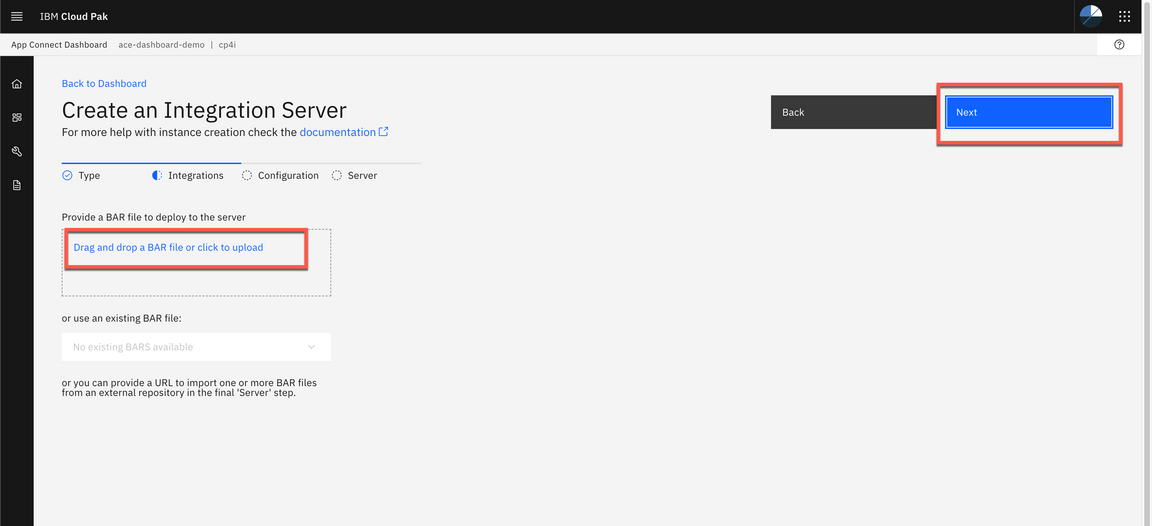
- You do not need to use the configuration package (configuration package contains the files that you can use for App Connect Enterprise works with Databases, Event Streams, etc) click Next.
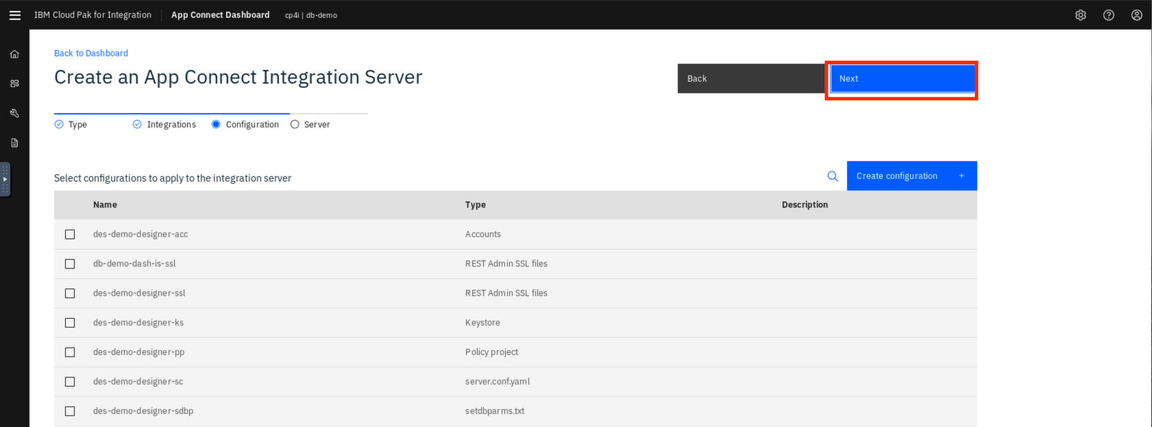
- On Create an Integration Server page, enter the Integration Server name as neworder (1). Then click Create (2).
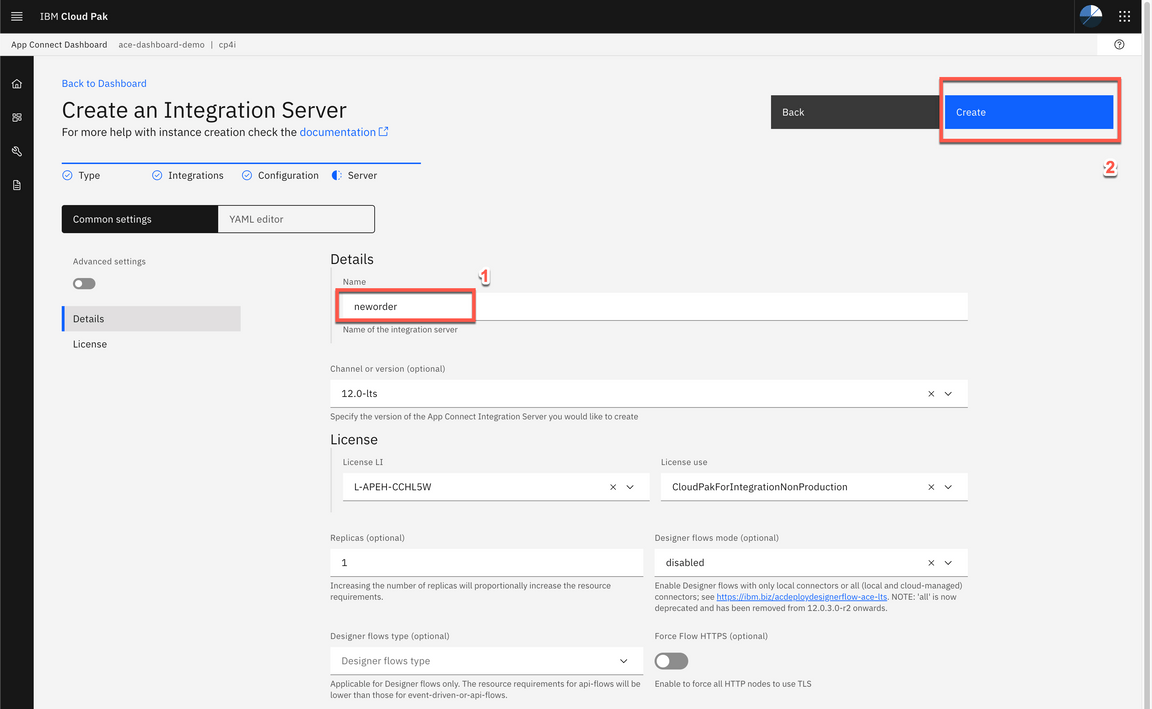
Great, your Integration Server was created!
Note: The deployment process takes up to 5 minutes, refresh the browser to see the BAR file deployed and started.
4 - Testing the API
- Here you can see the App Connect Enterprise Dashboard with the Integration Server neworder deployed and started. Click the neworder server icon.
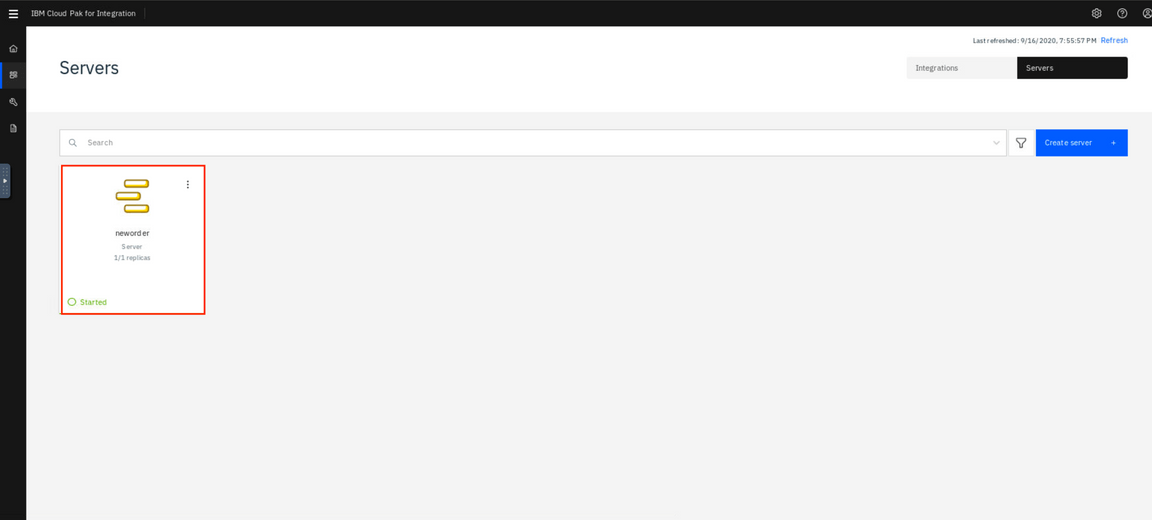
The next window shows the API in started state. Click on the tile to get the details.
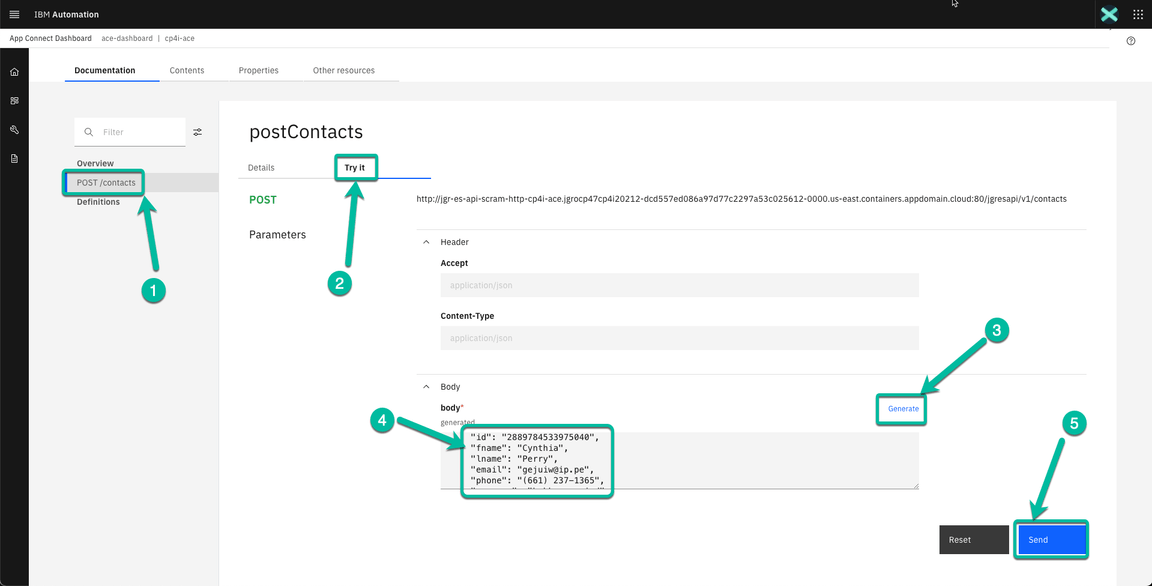
In the next page navigate to the operation implemented in your flow (POST /contacts). Then click on the Try it tab followed by the Generate hyperlink to generate some test data. Review the data generated and click the Send button.
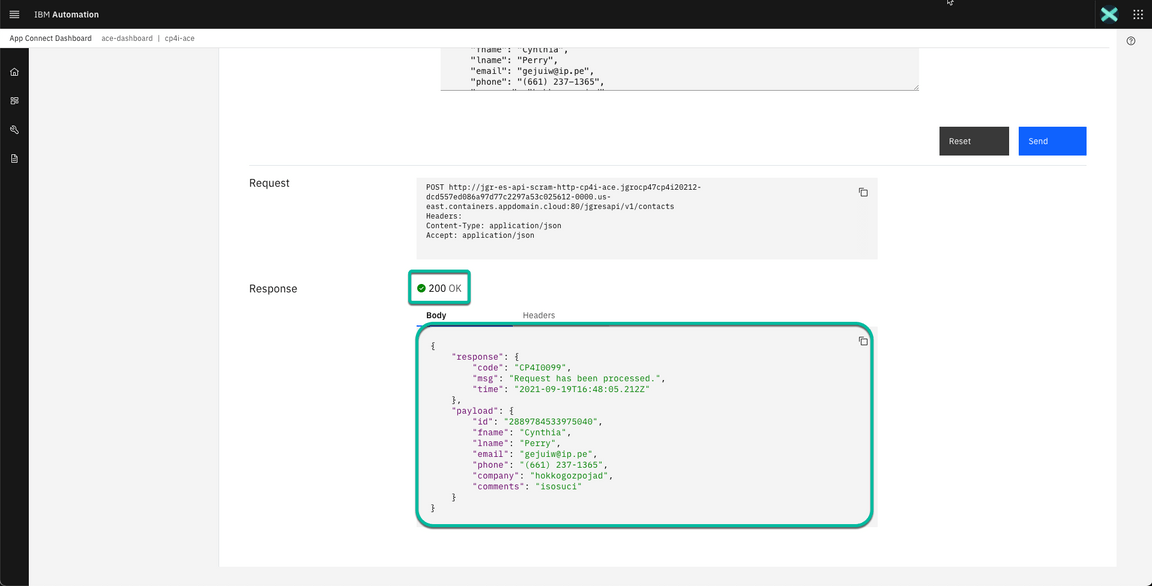
- After a moment you will get a response back. If everything is OK you will receive a 200 response code indicating the request was successful and the same payload you sent plus some metadata including a timestamp showing the request completed few seconds ago.
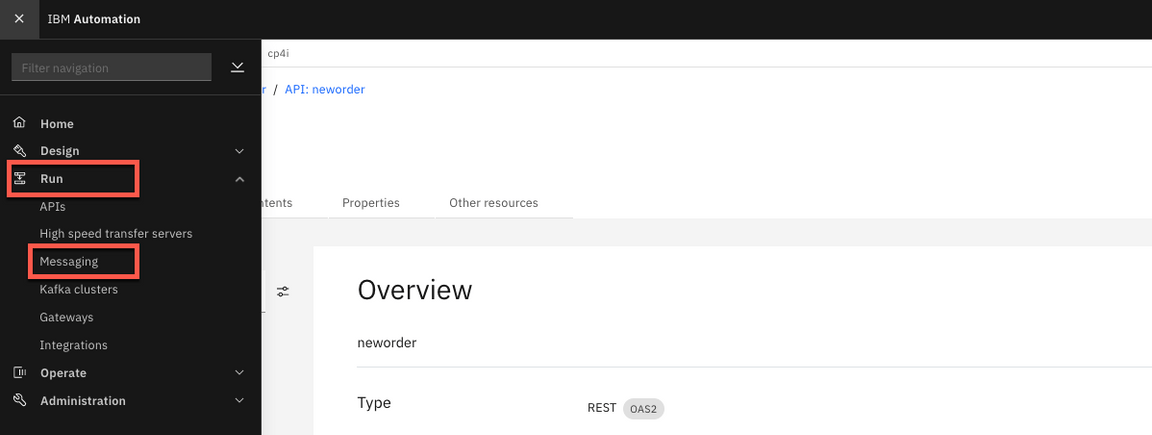
- Now, let’s check the message arrived in the NEWORDER queue in IBM MQ. Let’s use IBM MQ Console to check it. Open the Menu, and on Run section, click on Messaging.
6.Click Manage QMGRDEMO.
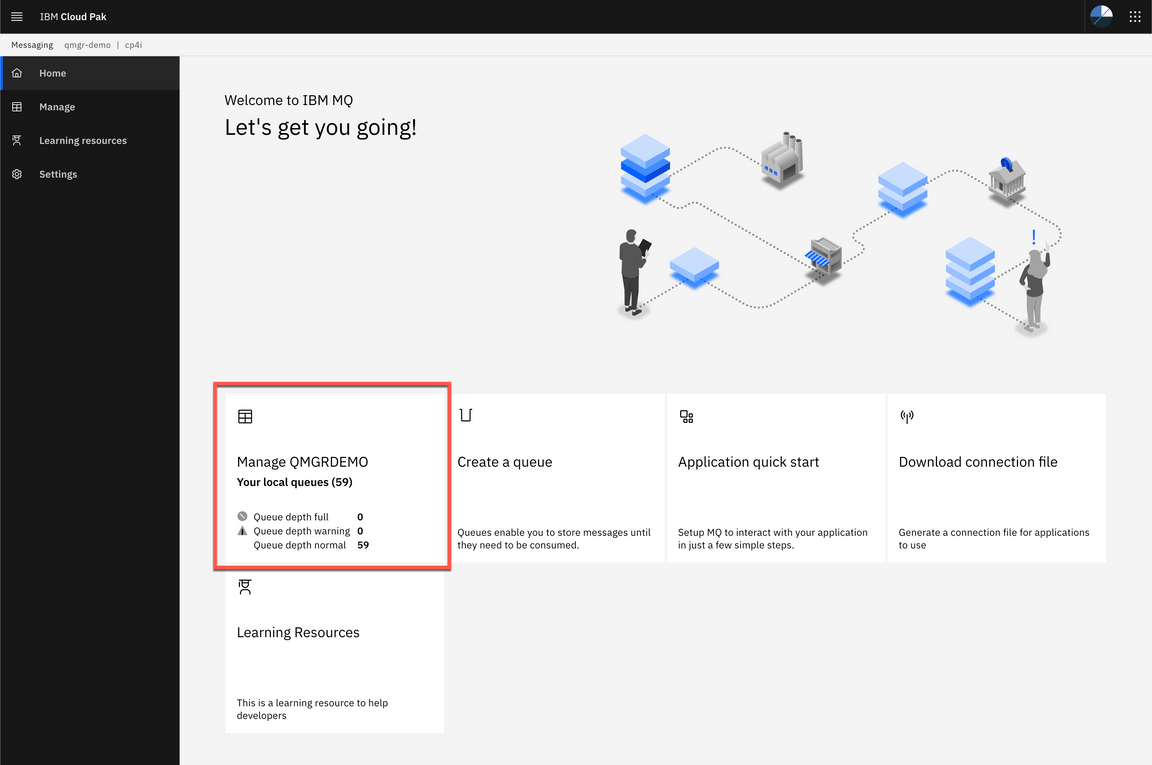
- Here you can see that a new message has arrived in CP4I.DEMO.API.Q queue.
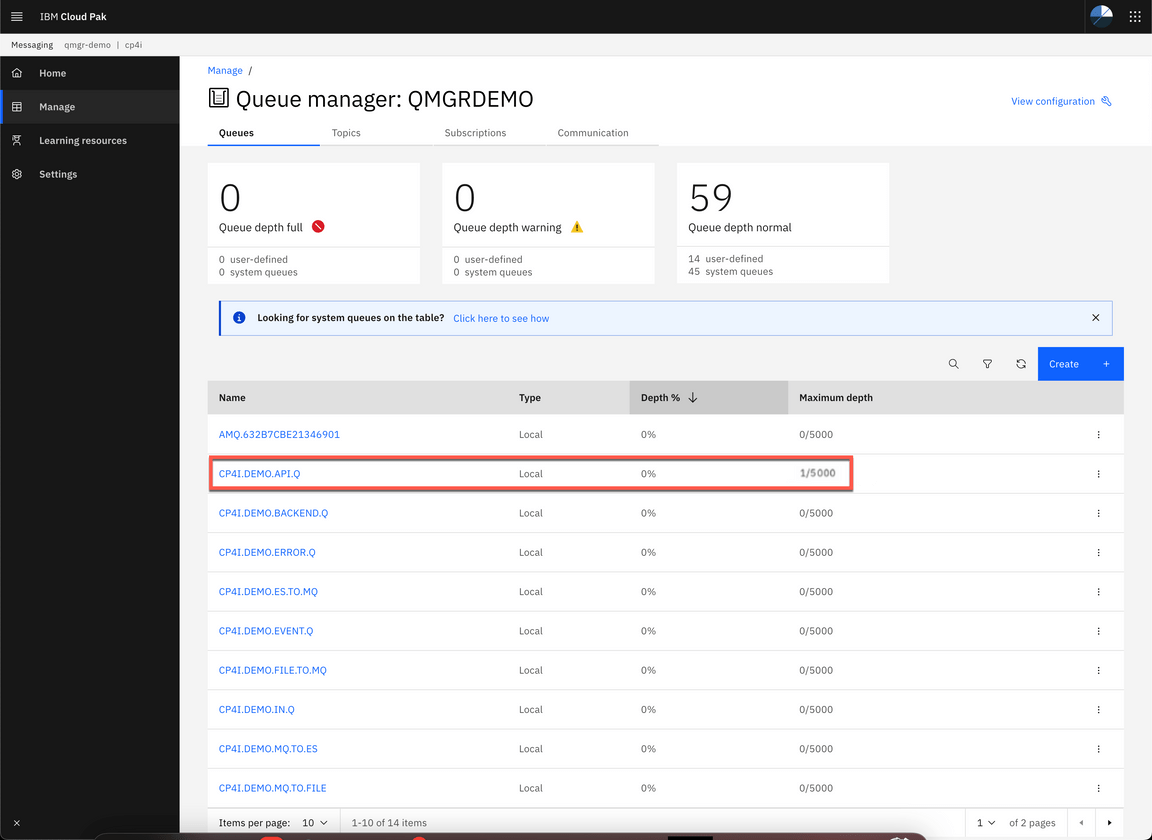
8.You are welcome, to click on the CP4I.DEMO.API.Q queue, to explore the message.
Congratulations! Here you completed this lab.
Summary
You have successfully completed this lab. In this lab you learned how to:
- Create an integration flow that connects to a message queue
- Deploy the integration flow as a container in Kubernetes
- Check the message using MQ Web Console
